Full Sharpe-Schoolfield model for fitting thermal performance curves
Source:R/sharpeschoolfull_1981.R
sharpeschoolfull_1981.RdFull Sharpe-Schoolfield model for fitting thermal performance curves
Arguments
- temp
temperature in degrees centigrade
- r_tref
rate at the standardised temperature, tref
- e
activation energy (eV)
- el
low temperature de-activation energy (eV)
- tl
temperature (ºC) at which enzyme is 1/2 active and 1/2 suppressed due to low temperatures
- eh
high temperature de-activation energy (eV)
- th
temperature (ºC) at which enzyme is 1/2 active and 1/2 suppressed due to high temperatures
- tref
standardisation temperature in degrees centigrade. Temperature at which rates are not inactivated by either high or low temperatures
Value
a numeric vector of rate values based on the temperatures and parameter values provided to the function
Details
Equation: $$rate= \frac{r_{tref} \cdot exp^{\frac{-e}{k} (\frac{1}{temp + 273.15}-\frac{1}{t_{ref} + 273.15})}}{1+ exp^{\frac{e_l}{k}(\frac{1}{t_l} - \frac{1}{temp + 273.15})} + exp^{\frac{e_h}{k}(\frac{1}{t_h}-\frac{1}{temp + 273.15})}}$$
where k is Boltzmann's constant with a value of 8.62e-05.
Start values in get_start_vals are derived from the data.
Limits in get_lower_lims and get_upper_lims are derived from the data or based extreme values that are unlikely to occur in ecological settings.
References
Schoolfield, R. M., Sharpe, P. J. & Magnuson, C. E. Non-linear regression of biological temperature-dependent rate models based on absolute reaction-rate theory. Journal of Theoretical Biology 88, 719-731 (1981)
Examples
# load in ggplot
library(ggplot2)
library(nls.multstart)
# subset for the first TPC curve
data('chlorella_tpc')
d <- subset(chlorella_tpc, curve_id == 1)
# get start values and fit model
start_vals <- get_start_vals(d$temp, d$rate, model_name = 'sharpeschoolfull_1981')
# fit model
mod <- nls_multstart(rate~sharpeschoolfull_1981(temp = temp, r_tref, e, el, tl, eh, th, tref = 20),
data = d,
iter = c(3,3,3,3,3,3),
start_lower = start_vals - 10,
start_upper = start_vals + 10,
lower = get_lower_lims(d$temp, d$rate, model_name = 'sharpeschoolfull_1981'),
upper = get_upper_lims(d$temp, d$rate, model_name = 'sharpeschoolfull_1981'),
supp_errors = 'Y',
convergence_count = FALSE)
# look at model fit
summary(mod)
#>
#> Formula: rate ~ sharpeschoolfull_1981(temp = temp, r_tref, e, el, tl,
#> eh, th, tref = 20)
#>
#> Parameters:
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> r_tref 1.61689 4.91091 0.329 0.7532
#> e 0.02815 1.01715 0.028 0.9788
#> el 1.44338 0.68857 2.096 0.0809 .
#> tl 28.53344 21.51361 1.326 0.2330
#> eh 19.24223 25.84740 0.744 0.4847
#> th 44.01635 1.62324 27.116 1.66e-07 ***
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
#>
#> Residual standard error: 0.1831 on 6 degrees of freedom
#>
#> Number of iterations to convergence: 38
#> Achieved convergence tolerance: 1.49e-08
#>
# get predictions
preds <- data.frame(temp = seq(min(d$temp), max(d$temp), length.out = 100))
preds <- broom::augment(mod, newdata = preds)
# plot
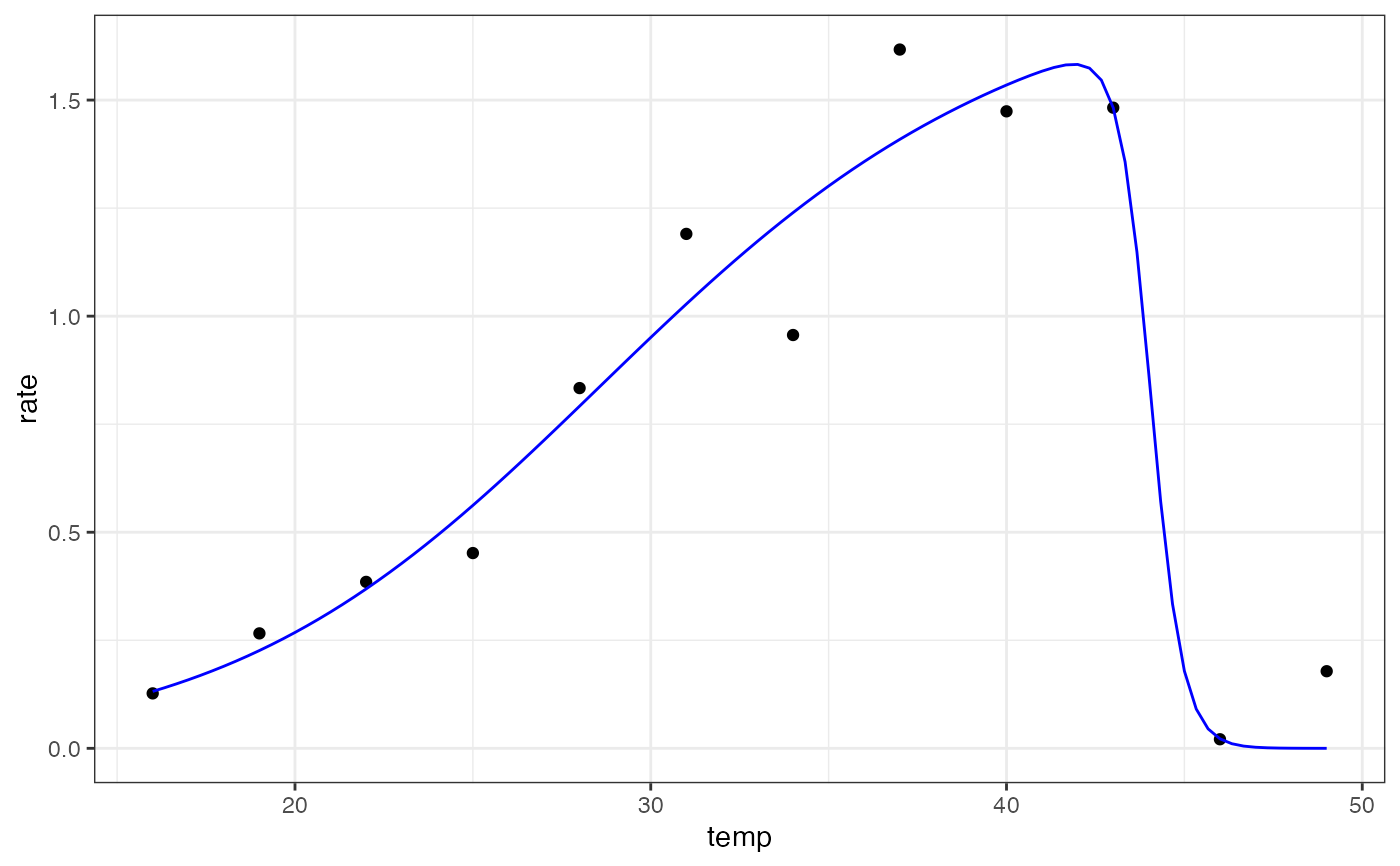
ggplot(preds) +
geom_point(aes(temp, rate), d) +
geom_line(aes(temp, .fitted), col = 'blue') +
theme_bw()